
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI) –
Artificial Intelligence in Modern Farming is revolutionizing agriculture by enhancing crop health monitoring, improving yield predictions, and optimizing supply chains. Discover how AI contributes to agriculture by automating processes, providing real-time data analysis, and enabling precision farming. Benefits of AI in agriculture include increased efficiency, reduced resource usage, and enhanced decision-making. From disease detection to supply chain optimization, AI is transforming the way we grow, manage, and distribute crops. Explore the future of farming with AI-driven innovations that are reshaping the agricultural landscape for a more sustainable and productive future.
Artificial Intelligence (AI); is revolutionizing multiple industries, and farming is no exception. As global population
growth places adding demands on food product, traditional agriculture styles alone cannot sustain the required affair
modern agriculture, stoked by AI, promises increased effectiveness, reduced waste, and lesser sustainability. This blog
explores the transformative impact of AI on farming, Role of Artificial Intelligence in Modern Farming, pressing its benefits, operations, and challenges.
Precision Agriculture One of the most significant advancements AI has brought to agriculture is precision farming.
This approach leverages AI- powered tools to dissect data and make precise opinions about planting, watering,
fertilizing, and harvesting crops.
How AI contributes in Agriculture:
1. Soil and Crop Monitoring –
AI algorithms dissect data collected by detectors and drones to determine the optimal
time for planting and harvesting. They also identify nutrient scarcities or pest infestations beforehand, enabling timely
intervention.
2. Weather Prediction and Monitoring-
Accurate rainfall soothsaying is critical for agriculture. AI models
prognosticate rainfall patterns more directly than traditional styles, helping growers plan their conditioning more and
reduce losses due to unanticipated rainfall changes.
3. Variable Rate Technology (VRT) –
AI systems companion ministry to apply diseases, fungicides, and water at
varying rates across a field, acclimatized to the specific requirements of different areas. This perfection reduces the
use of chemicals, minimizes environmental impact, and cuts costs.
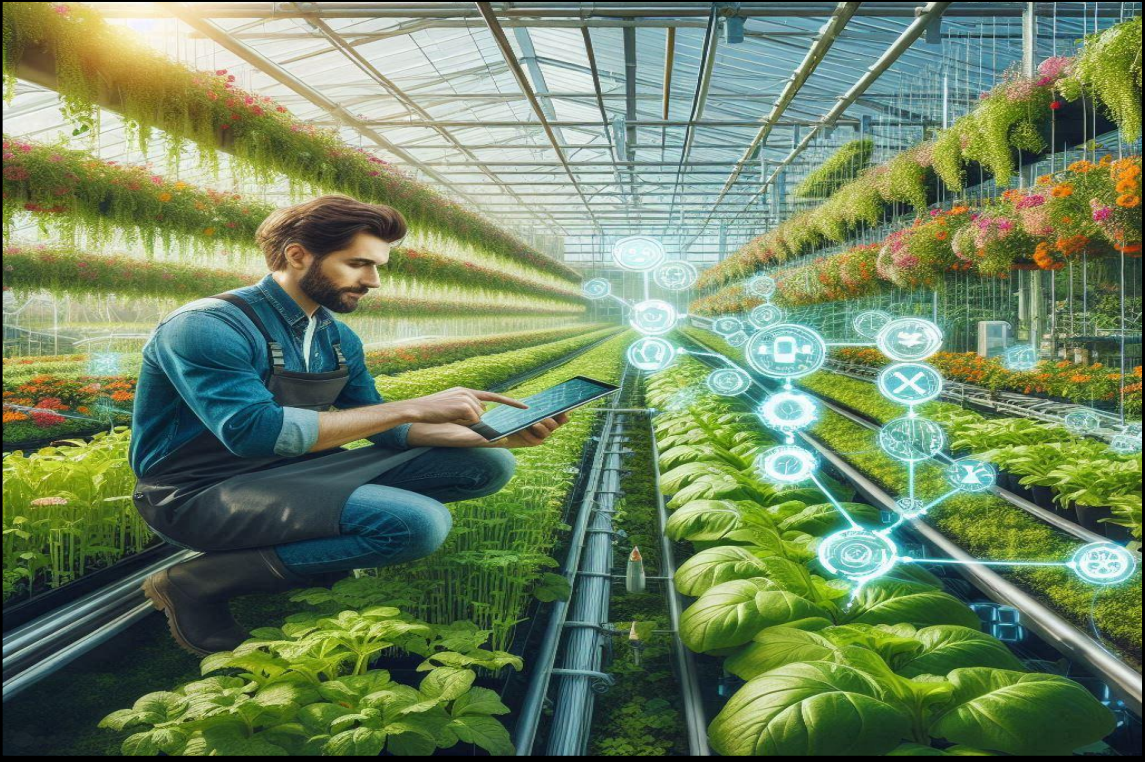
Crop Health Monitoring
AI- powered drones and satellite imagery are being employed to cover crop health on a large scale. These
technologies capture high- resolution images of fields, which are also anatomized using AI algorithms to identify
issues similar as conditions, pest infestations, or water stress.
1. Image Recognition –
AI systems with image recognition capabilities dissect images from drones or satellites to
identify unhealthy shops and diagnose problems, allowing for targeted treatments and reducing the need for mask
fungicide operation.
2. Predictive Analytics –
By assaying literal data and current conditions, AI can prognosticate implicit outbreaks of
pests, giving growers the chance to take preventative measures before a problem becomes wide.

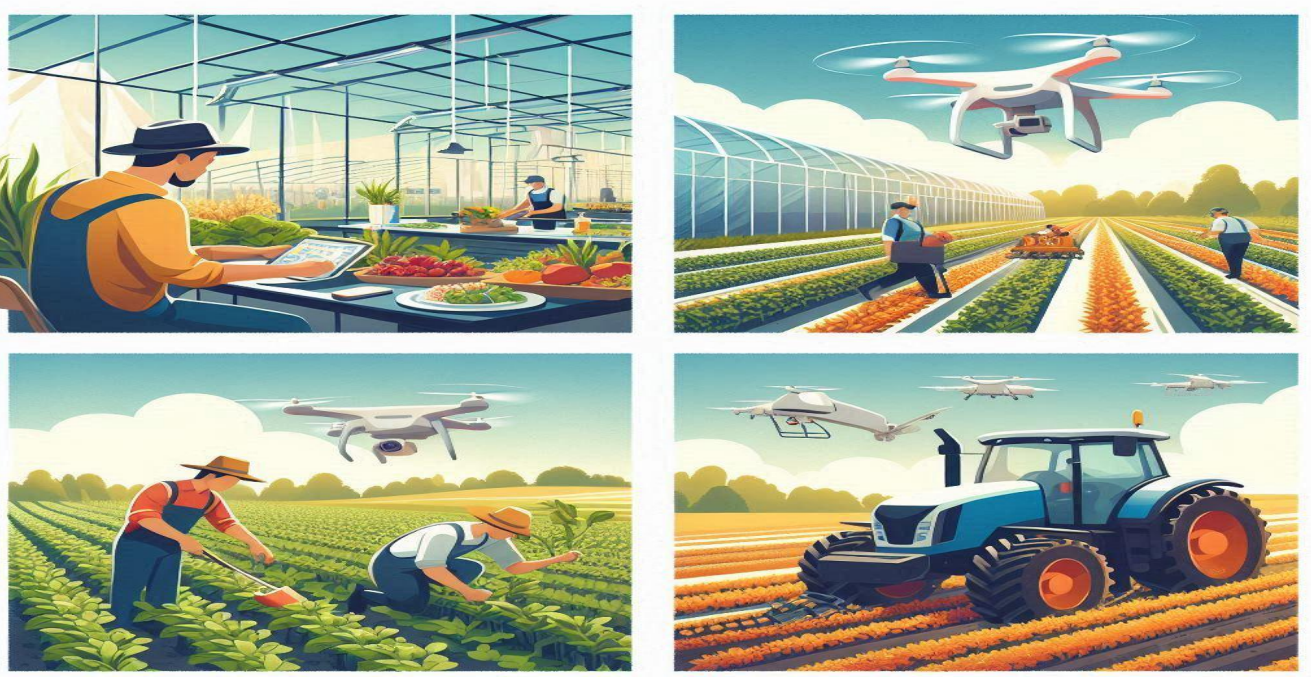
Autonomous Machinery
AI is driving the development of independent ministry that can perform colorful agriculture tasks with minimum
mortal intervention.
1. Autonomous Tractors-
Self- driving tractors equipped with AI can perform tasks similar as furrowing, planting,
and harvesting. These tractors can operate24/7, adding productivity and reducing labor costs.
2. Robotic Harvesters –
AI- powered robots can pick fruits and vegetables. These robots work lifelessly and
handle delicate crops with perfection, reducing damage and waste.
3. Weed Control Robots –
AI- driven robots identify and remove weeds with high delicacy, reducing the need for
chemical dressings and promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
Livestock Management
AI’s influence extends to beast operation, furnishing tools to cover health, optimize feeding, and ameliorate
parentage programs.
1. Health Monitoring;
AI systems cover the health and gesture of livestock through wearable devices and
cameras. These systems descry signs of illness or stress beforehand, allowing for timely interventions and
perfecting Animal welfare.
2. Feed Optimization;
AI analyzes data on feed consumption and animal growth to optimize feeding strategies,
icing that creatures admit the right nutrients at the right time, perfecting productivity and reducing waste.
3. Parentage Programs;
AI algorithms dissect inheritable data to identify the best breeding pairs, enhancing the
inheritable quality of animal and perfecting traits similar as milk product, disease resistance, and growth rates.
Supply Chain Optimization
AI enhances the agricultural supply chain, from farm to fork.
1. Demand forecasting –
AI analyzes market trends and consumer gesture prognosticate demand for colorful crops
and livestock products. This helps growers plan their product and reduce surplus or Shortages.
2. Logistics and Distribution –
AI optimizes logistics and distribution networks, icing that fresh yield reaches
consumers snappily and efficiently. This reduces food waste and ensures better prices for growers.
3. Quality Control –
AI systems check produce for quality and safety, icing that only the best products reach
consumers, enhancing food safety and reducing the threat of recalls.

Benefits of AI in Agriculture
The integration of AI in farming offers multiple benefits
1. Increased effectiveness –
AI automates numerous labor- ferocious tasks, allowing growers to concentrate on
strategic opinions and adding overall farm effectiveness.
2. Cost Reduction –
Precision farming and autonomous machinery reduce the need for inputs similar as
fertilizers, fungicides, and labor, cutting costs for growers.
3. Sustainability –
AI enables more precise use of resources, reducing environmental impact and promoting
sustainable agriculture practices.
4. Improved Yields –
AI-driven perceptivity help growers make better opinions, leading to advanced crop yields
and better quality produce.
5. Enhanced Food Security-
By adding effectiveness and productivity, AI helps meet the growing demand for
food, contributing to global food security.
Challenges and Considerations
While AI holds great promises for ultramodern farming, there are challenges and considerations to address;
1. Cost of Implementation –
The original investment in AI technology can be high, which may be a hedge for small scale growers.
2. Data Privacy –
The collection and use of data by AI systems raise Concerns about data privacy and Ownership.
3. Technical Skills –
growers need to acquire new skills to operate and maintain AI systems, which may require
training and education.
4. Ethical Considerations –
The use of AI in livestock management raises ethical questions about animal welfare and
the extent of robotization in farming

Conclusion
AI is transforming modern agriculture, offering results to some of the most pressing challenges in the
field. From precision agriculture and crop health monitoring to autonomous machinery and livestock management, AI
enhances effectiveness, sustainability, and productivity in farming. While there are challenges to overcome, the implicit
benefits of AI in agriculture are immense, promising a more sustainable and secure future for global food production.
As technology continues to evolve, the integration of AI in farming will probably come indeed more sophisticated,
farther revolutionizing the way we grow and manage food.
In summary, AI’s part in modern agriculture is multifaceted and transformative. It offers tools and perceptivity that
were preliminarily unimaginable, helping to insure that farming can meet the requirements of a growing population in a
sustainable and effective manner. As the agriculture sector continues to embraces AI, we can expect even more
innovative solution to emerge, driving the future of farming forward.
For more information on implementation of AI in modern agriculture you can visit our other blogs on
Biotechnology and Biotechnology application in agriculture
Nanotechnology and Application of nanotechnology in Agriculture




